
Source: Shutterstock
As diagnostic demand continues to rise globally, healthcare markets in Asia—including Singapore, Malaysia, and India—are showing increasing interest in medical solutions that can meet this growing need. Regions such as India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan have high population densities but lack adequate per capita healthcare infrastructure. As a result, they are facing a dual disease burden, with infectious diseases like tuberculosis and malaria on the rise alongside chronic conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
In this context, countries across Asia are seeking cost-effective point-of-care (POC) diagnostic solutions capable of supporting large-scale testing. There is also strong potential demand for healthcare solutions that improve accessibility, such as mobile health and telemedicine. However, significant disparities remain, including gaps in healthcare service access between urban and rural areas, as well as differences in the capacity of public healthcare institutions across countries.
The Ongoing Challenge of Tropical Disease Diagnostics in Asia

Source: Shutterstock
In parts of Asia, tropical infectious diseases persist due to factors such as climate, environment, and healthcare system challenges. The hot and humid tropical climate, with high temperatures and heavy rainfall year-round, creates ideal conditions for mosquito activity. Rapid urbanization has led to the formation of slum areas where poor sanitation and drainage result in frequent water stagnation, accelerating the spread of infectious diseases. In particular, structural issues within the healthcare system remain a key challenge that must be addressed in these regions.
These challenges often lead to delays in early diagnosis, which can contribute to the spread of diseases at the region level. As a result, many Asian countries have a strong demand for simple, automated point-of-care (POC) diagnostic technologies to address infectious disease response, infrastructure improvement, and healthcare disparities. There is also growing interest in innovative technologies that can enhance diagnostic efficiency, prompting active adoption efforts.
Insights into Asia’s Diagnostic Trends from WHX Kuala Lumpur

Source: Shutterstock
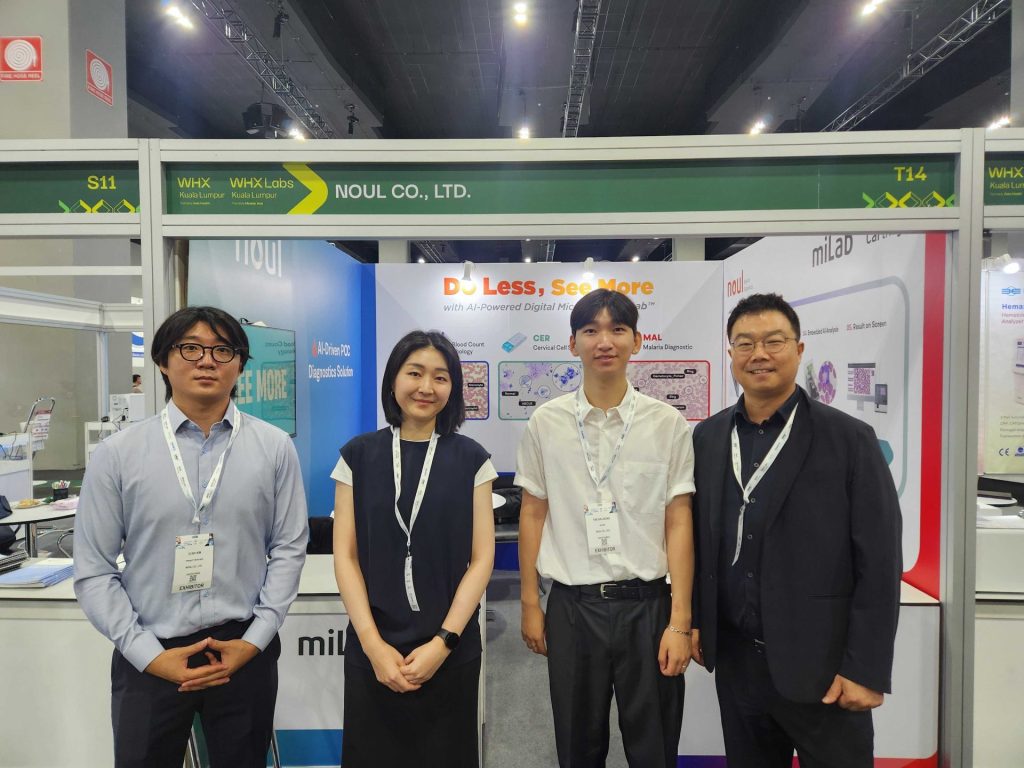
NOUL, committed to delivering high-quality healthcare services to more people through innovative technology, participated in WHX ASIA 2025, Asia’s largest healthcare exhibition. At the event, NOUL reviewed the latest diagnostic trends and analyzed the market to develop strategies for entering Asian and global markets. Additionally, NOUL introduced miLab™, a solution designed to improve diagnostic environments in Asia, where demand for point-of-care (POC) technologies is growing rapidly.
At WHX ASIA 2025, NOUL operated a booth and engaged in conversations with various stakeholders in the diagnostics industry, gaining valuable insights through these interactions.
- Some regions in Asia still face challenges with tropical infectious diseases. In the case of malaria, rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) are widely used, but they have limitations in accurately detecting low-density and asymptomatic infections, which increases the risk of false-negative results.
- Basic blood tests such as complete blood count (CBC) are largely dependent on central hospitals, with many primary care facilities and rural health centers lacking CBC equipment altogether.
- While microscopy provides high-quality diagnostic results, the shortage of skilled personnel and time constraints have led to growing interest in high-performance point-of-care (POC) devices that can deliver comparable accuracy.
International health organizations are actively advancing initiatives to eliminate infectious diseases in Asia, including the WHO’s “Malaria Elimination Initiative” and the Mekong Malaria Elimination (MME) project. Additionally, organizations such as WHO, ADB, and UNDP prioritize strengthening diagnostic capabilities at primary healthcare centers across Asia, actively promoting opportunities to introduce low-cost, high-efficiency diagnostic platforms as a key strategy for health system improvement.
miLab™’s Diagnostic Performance Validated Through Field Experience

Source: noul
The Asian diagnostic market, as experienced on the ground, is actively seeking innovative diagnostic technologies to meet rapidly growing demand. NOUL’s automated diagnostic platform, miLab™, has attracted attention as an optimal solution that addresses these needs. Especially in Asia, where demand for point-of-care (POC) diagnostics is high, miLab™ is recognized as a high-performance, portable device that can be used in resource-limited settings without requiring specialized expertise, enabling expert-level diagnostics at the point of care.
NOUL’s proprietary solid-based staining technology (NGSI, Next Generation Staining and Immunostaining) integrates the entire microscopy diagnostic process without requiring components such as pumps, tubing, or reagents that are essential in traditional liquid staining methods. Compared to liquid staining, it reduces the amount of staining reagent needed by 99%, minimizing environmental impact. Additionally, on-device AI analyzes samples to deliver highly accurate diagnostic results, minimizing human error and ensuring consistent analysis outcomes.

Source: noul
At WHX ASIA 2025, NOUL showcased its products under the slogan “Do Less, See More.” This slogan reflects miLab™’s core capabilities of simplifying the testing process through innovative technology and delivering precise, consistent results via AI analysis. Visitors to NOUL’s booth who experienced miLab™ firsthand gave positive feedback on its fully automated testing system, compact device design, and AI-driven high-quality results. In particular, they expressed strong interest in miLab™’s ability to automatically store and manage diagnostic data, enabling seamless linkage from diagnosis to treatment in situations where patient data had previously been fragmented and hindered follow-up care.
Transformative Impacts of miLab™ on Asia’s Diagnostic Landscape
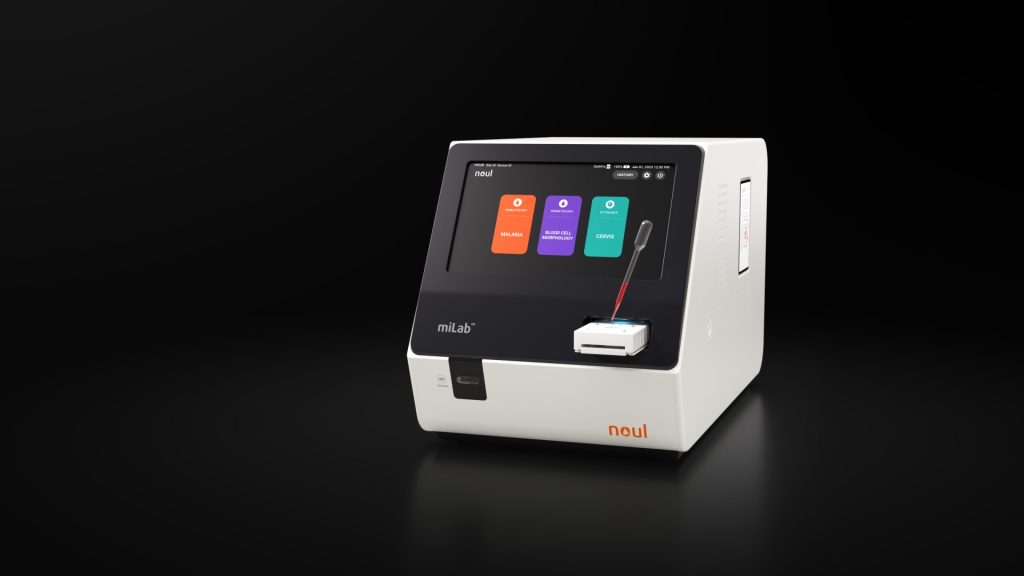
Source: noul
miLab™ offers functions for malaria diagnosis, blood analysis, and cervical cancer cell screening. By automating the testing process, it enhances diagnostic efficiency, enabling fast and accurate results for patients.
- Some regions in Asia continue to experience malaria outbreaks, with challenges arising in detecting pfhrp2/3 gene deletions, especially in areas with low parasite density. miLab™ MAL offers highly accurate diagnosis of malaria infections caused by P. falciparum and P. vivax, demonstrating performance comparable to traditional optical microscopy.
- Additionally, miLab™ BCM has obtained certifications in several Asian countries, including Vietnam and Thailand, aiming to address healthcare disparities in these regions and support the expansion of CBC and early blood cancer screening at primary care clinics and health centers.
- Additionally, since cervical cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths among women in Southeast Asia, miLab™ CER can serve as an optimal solution to expand screening by reducing dependence on skilled personnel and enabling seamless testing through diagnosis.
NOUL’s participation in WHX ASIA 2025 marked a significant milestone in the full-scale entry of miLab™ into the Asian market. With its compact design enhancing medical accessibility and streamlined diagnostic processes powered by AI that reduce reliance on skilled personnel, miLab™ is expected to contribute not only to Asia but also to global health equity. Following its expansion into Africa, the Middle East, and Europe, Noul aims to aggressively expand into the Asian market, addressing global healthcare disparities and enabling high-quality medical services for all.
If you’re curious about how NOUL’s miLab™ platform can help address global healthcare disparities, click the link to learn more!

