
Source: shutterstock
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is one of the most essential diagnostic procedures for assessing a patient’s health status. Because CBC testing requires high accuracy, throughput, and strict quality control, it is typically performed in centralized laboratories equipped with large automated analyzers and skilled laboratory personnel. While this model delivers reliability, it also introduces limitations in speed, sample handling, and point-of-care accessibility—especially when rapid decisions are critical.
For pediatric, neonatal, and critically ill patients, where sample volume is limited, diagnostic delays frequently occur due to re-draws or specimen transport time. Such delays can directly impact clinical decisions—including early antibiotic initiation, fluid management, or emergency referral—risking the loss of precious treatment time. They also increase caregiver anxiety and clinical workload. As healthcare systems increasingly require faster and closer-to-patient diagnostics, the paradigm is shifting from centralized testing toward Point-of-Care diagnostics. The next phase of CBC testing is emerging right beside the patient.
Diagnostics Moving Beyond the Lab — The Rise of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT)
Source: shutterstock
Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) has become a defining trend in modern diagnostics. By enabling rapid testing outside the centralized lab, POCT reduces delays, accelerates clinical decision-making, and supports diagnostic equity across diverse healthcare settings.
The WHO and FIND have emphasized the decentralization of diagnostics as a global priority (FIND 2023). This shift is no longer limited to low-resource countries—regional hospitals, satellite labs, outpatient clinics, and general practitioners in high-income nations are adopting POCT solutions at increasing speed.
However, CBC testing presents unique challenges:
- smear quality must be consistent,
- staining must be uniform,
- cell morphology assessment must be accurate,
- and results must match laboratory standards.
Conventional POCT devices have struggled to meet these criteria. As a result, the market now demands POCT solutions capable of accurate, image-based, morphology-driven CBC analysis.
According to Mordor Intelligence (2024), the Point-of-Care Hematology Diagnostics market is projected to grow from USD 2.27 billion in 2025 to USD 3.63 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 9.8%. This shift signals not just technological progress but a fundamental change in how and where clinical decisions are made.
At the center of this transformation is a new generation of AI-powered, slide-based CBC platforms designed to deliver lab-quality hematology at the point of care.
Automating Microscopy — The Technological Leap Behind miLab™ BCM
Source: noul
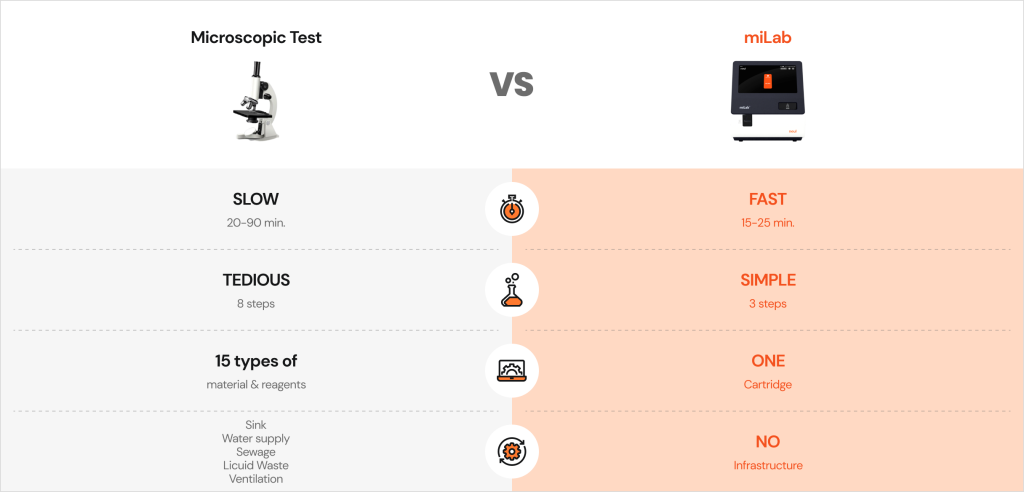
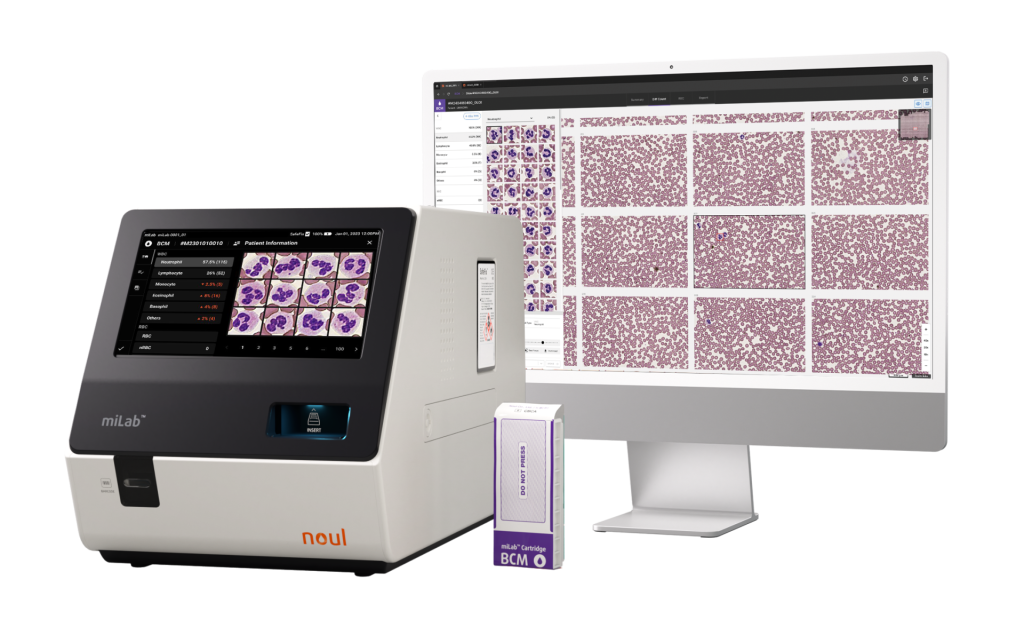
Traditional microscopy requires multiple manual steps—smear preparation, stain application, drying, and reviewing cells field-by-field. Results inevitably vary with operator skill, environmental conditions, and stain consistency, and interpretation fatigue increases with sample volume. miLab™ BCM automates this entire smear–stain–image–analyze workflow inside a compact device and cartridge.
Using only 5 μL of blood, the system:
- performs optimized automated smearing,
- applies NGSI (Next-Generation Staining & Immunostaining) liquid-free solid staining,
- captures high-resolution digital images, and
- executes on-device AI algorithms to generate immediate CBC and morphology results.
NGSI eliminates stain variability caused by humidity or technique, producing consistent color density without liquid reagents or wastewater. This ensures reliable, slide-based CBC analysis across any care setting.
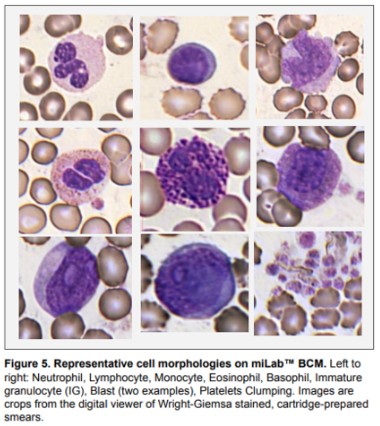
Unlike flow cytometry–based analyzers, miLab™ BCM merges slide-based morphology with AI-powered digital microscopy, delivering both quantitative results and image-level transparency. When needed, slides can be re-evaluated using manual microscopy. The upcoming v1.3 enhances cell boundary recognition, stain uniformity, WBC focus stability, and RBC morphology accuracy—moving the system closer to a reference-level POC hematology analyzer capable of supporting rapid clinical decisions.
Clinical Evidence Demonstrating Proven Reliability
The platform’s analytical performance has been validated across diverse patient groups and clinical settings, confirming that an AI-driven slide-based CBC system can meet laboratory standards.
In a 2025 clinical performance evaluation, the device was compared directly with the Sysmex XN-series. Key CBC parameters—including WBC, RBC, Hb, HCT, and PLT—showed correlations of r = 0.90–0.96. WBC differentials such as Neutrophils and Lymphocytes exceeded r > 0.93, improving to r ≥ 0.95 with the v1.3 algorithm. The system maintained this performance even with micro-samples under 5 μL from infants and toddlers under two years of age—groups that often require repeat sampling with high-volume analyzers.
These findings were reinforced at the LMCE 2025 (Laboratory Medicine Congress & Exhibition) and 66th KSLM (Korean Society for Laboratory Medicine) Annual Meeting, where a whole-blood Method Comparison evaluated CBC parameters vs. the Sysmex XN-series, and differential results vs. manual microscopy by expert technologists. High agreement was observed across CBC parameters. For clinically important abnormal cells, the system achieved r = 0.957 for IG and r = 0.976 for Blast cells.
These outperform large analyzers (e.g., Sysmex IG r = 0.791) and highlight the platform’s strength in digital morphology.
Source: LMCE 2025 Poster, Noul & Asan Medical Center
Together, the data show that this is not merely an automated CBC device but a clinically validated AI microscopy system that aligns with both laboratory analyzers and human experts. With paired high-quality cell images, clinicians can immediately review flagged abnormalities, accelerating decision-making—a critical advantage in time-sensitive frontline settings.
A New Standard for Hematology — One Drop, Countless Possibilities
Source: noul
miLab™ BCM goes beyond consolidating CBC, staining, imaging, and AI analysis into a single automated workflow—it redefines how hematology can be delivered across the care spectrum. The combination of on-device AI and NGSI enables clinicians to obtain standardized, reproducible, and image-verified CBC data, anywhere.
This opens pathways for consistent hematology testing across:
- primary care clinics
- pediatric centers
- mobile diagnostic units
- satellite labs in large laboratory networks
The remote Viewer accelerates collaboration and expert review, helping overcome workforce constraints and bridging the gap between central labs and distributed care environments.
Ultimately, this platform represents the next evolution of the hematology ecosystem—improving data flow, diagnostic speed, and patient experience with the power of a single drop of blood. As diagnostics move beyond the traditional laboratory, AI-enabled, slide-based CBC systems stand poised to reshape global access to reliable hematology services.
Now, experience the Future of CBC at the Point of Care – Request a miLab™ BCM demo today and discover how AI-driven digital hematology can transform your diagnostic workflow.

