Introduction
 Source: Deviantart
Source: Deviantart
Red blood cells (RBCs) transport oxygen throughout the body. They usually appear as uniform and biconcave discs. However, significant variations in size, shape, or structure can be a sign of underlying health issues. Among these, anisocytosis (irregular cell size) and poikilocytosis (irregular cell shape) are especially telling, as they commonly accompany conditions that range from nutritional deficiencies to chronic organ dysfunction.
The identification of RBC shape and other deviations helps healthcare professionals diagnose early-stage diseases. Standard assessments such as the Complete Blood Count (CBC) and Peripheral Blood Smear (PBS) are instrumental in the detection of abnormal red blood cell morphology, which prompts timely therapeutic interventions.
For more details on CBC testing, visit CBC Test Normal Ranges & 5 WBC Counts on NOUL’s website.
Understanding Anisocytosis : RBC Size
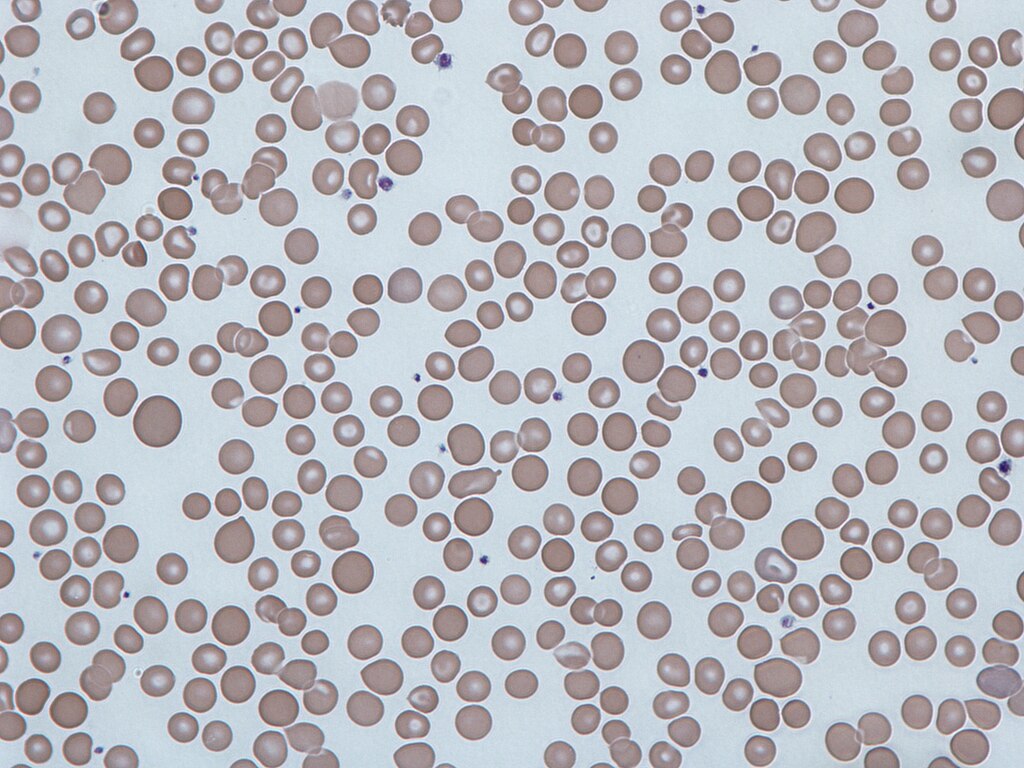 Source: Wikimedia Commons
Source: Wikimedia Commons
Anisocytosis is a major example of RBC abnormalities. It is characterized by notable discrepancies in RBC size. Laboratory evaluations commonly use Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW) to measure the extent of these size variations.
Some of the conditions that present with elevated RDW include:
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Pernicious anemia.
- Deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12.
Additionally, certain bone marrow disorders, such as myelodysplastic syndromes, can exacerbate these irregularities.
From a clinical perspective, anisocytosis usually presents with anemia-like symptoms (e.g., fatigue, pallor, shortness of breath). Spotting this abnormal RBC morphology early can guide healthcare providers toward more targeted nutritional or medical interventions.
To learn more about CBC and smear-based diagnostics, see CBC and Peripheral Blood Smear Test on NOUL’s blog.
Understanding Poikilocytosis : RBC Shape
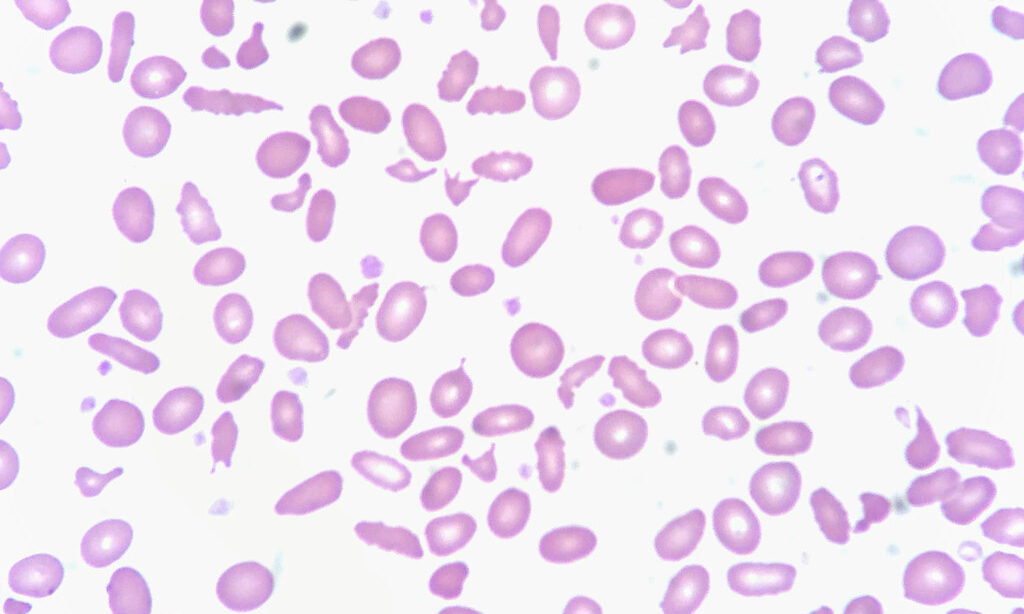 Source: Flickr
Source: Flickr
Poikilocytosis focuses on abnormal RBC shape, which makes it another key indicator of RBC abnormalities.
Common abnormal shapes include:
- Spherocytes.
- Elliptocytes.
- Target cells.
- Sickle cells.
These morphological shifts can point to specific disorders. For example, hereditary spherocytosis commonly produces spherocytes. On the other hand, sickle cells are hallmarks of sickle cell anemia.
Clinical manifestations of poikilocytosis generally mirror anemia (fatigue, weakness, and potential organ complications). The identification of abnormal red blood cell morphology can pinpoint conditions such as liver disease (target cells), thalassemia (target and other cell shapes), or inflammatory disorders.
Consult this article to learn more about this topic.
Implications of Anisocytosis and Poikilocytosis
When anisocytosis and poikilocytosis occur together, they shed some light on various types of abnormal RBC shape and size. This provides a clear window into a patient’s health.
Many conditions (e.g., nutritional deficiencies, hereditary disorders, chronic liver or kidney disease) give rise to such RBC abnormalities. Therefore, when we connect the specific RBC changes to underlying causes, clinicians will be able to expedite diagnosis and personalize treatment strategies.
The following table highlights RBC deviations and their common associations:
Rapid treatment of these abnormalities can significantly enhance patient outcomes. More detailed information on anemia can be found at MedlinePlus: Anemia.
NOUL’s miLab™ BCM
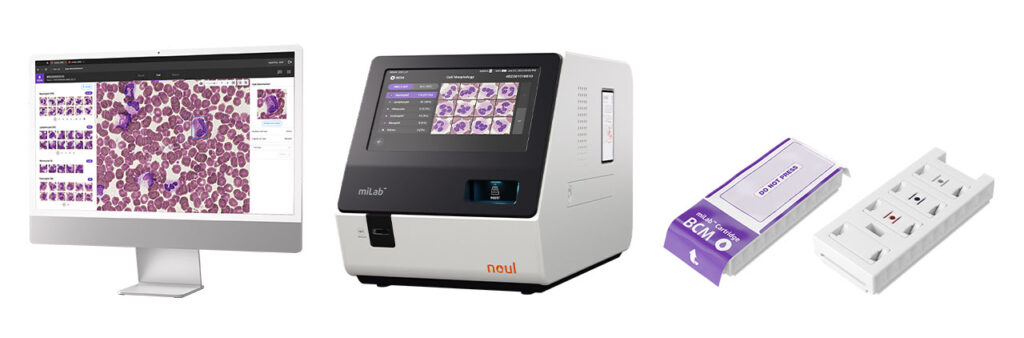 Source: NOUL
Source: NOUL
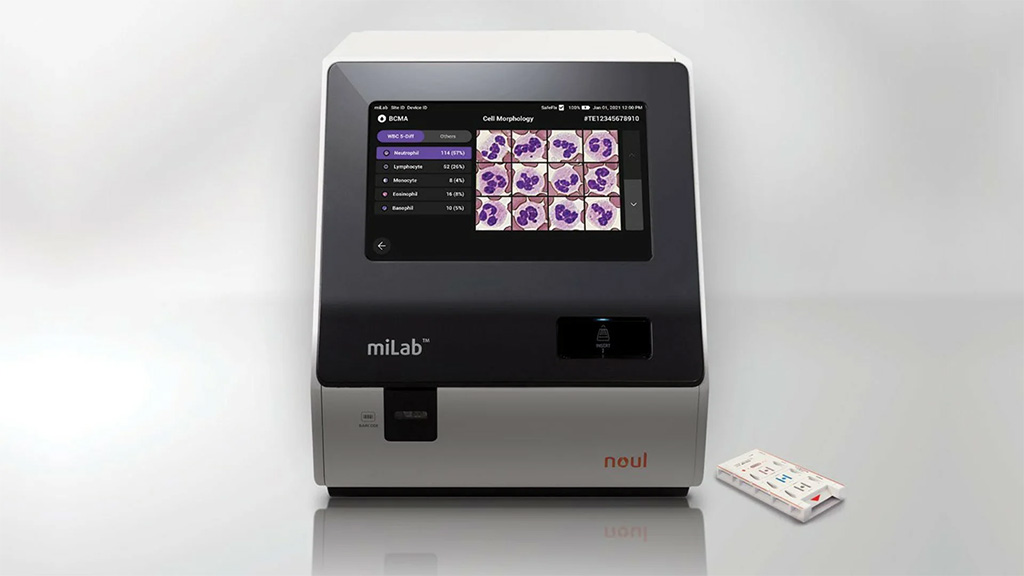
To enhance blood analysis accuracy, NOUL’s miLab™ BCM combines advanced AI algorithms with blood count & morphology data, offering insights that can aid in detecting conditions like anisocytosis and poikilocytosis. This portable solution reduces human error by automatically classifying cells based on size and shape, helping ensure that morphological abnormalities, including irregular red blood cell shapes, don’t go unnoticed.
In regions with limited diagnostic infrastructure, miLab™ BCM is excellent for the local medical facilities to obtain precise and immediate results. The combination of high-resolution image capture with robust data processing makes it possible for the platform to deliver consistent evaluations of abnormal RBC morphology. This capability makes it possible for clinicians to implement timely interventions for conditions such as iron-deficiency anemia, sickle cell disease, and other chronic disorders.
If you’re seeking an innovative edge in RBC analysis, explore miLab™ BCM Product Page. For direct inquiries on the integration of miLab™ BCM into your healthcare setting, visit NOUL’s Inquiry Page.
Conclusion
 Source: NOUL
Source: NOUL
The early recognition of red blood cell abnormalities such as anisocytosis and poikilocytosis can transform patient care. The use of advanced solutions such as NOUL’s miLab™ BCM gives healthcare providers the ability to quickly interpret abnormal red blood cell morphology.
As medical technology continues to evolve, it’s more important than ever to stay informed about the use of next-generation diagnostic tools.

