Leukemia is a life-threatening form of blood cancer. It affects the bone marrow, causing disruption to normal blood cell production. If left untreated, leukemia can lead to severe depletion of these vital blood cells. White blood cells, in particular, are a concern as these cells usually protect against infections.
Like all cancers, leukemia continues to progress over time. An early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to combating the depletion of blood cells. Often, this takes the form of leukemia blood count results, which show dramatic declines or unusual morphology in blood cells.
Modern advances in AI technology now allow us to rapidly diagnose leukemia without sacrificing accuracy. NOUL’s miLab™ BCM is an innovative platform that can perform a leukemia blood smear in a matter of minutes – a game-changer for diagnostic precision and healthcare outcomes.
Understanding Leukemia and White Blood Cell Count
Source: DALL·E
What is a White Blood Cell Count?
In leukemia, a complete blood count (CBC) is the primary method for detecting the condition. A white blood cell (WBC) count measures the number of white blood cells in a sample of blood, typically reported as cells per microliter.
The normal range is between 4,500 and 11,000 cells per microliter. White blood cells are crucial for immune health, as they play a key role in fighting infections. They identify and destroy pathogens, helping to protect the body from disease and maintain overall health.
How Leukemia Affects White Blood Cell Count
Leukemia can affect white blood cells (WBCs) in seemingly counterintuitive ways. Abnormal WBCs begin to grow and proliferate uncontrollably, replacing the standard WBCs. These abnormal WBCs do not perform the same functions as standard WBCs – in fact, they can either crowd them out or suppress their production entirely.
As a result, leukemia CBC results for white blood cells can either appear high or low, depending on if there’s an overproduction or suppression of healthy cells. Different types of leukemia have different white blood cell count ranges:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) causes a dramatic increase in WBCs. Often, the levels exceed 30,000 cells per microliter – even going as high as 100,000 cells per microliter in some cases.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) mostly affects mature lymphocytes, causing a gradual increase in their numbers. The expected leukemia white cell count range is between 20,000 to 100,000 cells per microliter – gradually increasing over time.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) can either present with a low (below 4,000 cells per microliter) due to marrow suppression or an extremely high count, depending on the subtype and progression of the disease.
Diagnosis with Leukemia Blood Smear Analysis
Source: Wikimedia Commons
A leukemia blood smear is a diagnostic procedure that analyses a blood sample for abnormalities in cell morphology. Currently, it involves extensive lab work, preparing the slide, staining the sample, and visualizing it under a microscope.
Specialists then look for changes in the cell structure of WBCs that are characteristic of leukemia. It’s the only way to diagnose specific forms of leukemia after the initial CBC results confirm WBC count changes.
Here’s a complete overview of the potential morphological changes:
Leukemia CBC Results
A complete blood count for leukemia is a standard part of the diagnostic process. CBC tests are routine in hospitals, measuring the levels of blood components, including:
- White Blood Cells (WBCs). Indicate either an infection or leukemia.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs). Carry oxygen in the blood. Often low in leukemia patients.
- Involved in clotting. Frequently reduced in leukemia patients, leading to bleeding issues.
- Carries oxygen within the RBCs – usually low in leukemia.
Leukemia blood count results are often altered. As mentioned, the most obvious change is either an elevated or drastically low WBC count. Other changes include low RBC count, low hemoglobin (anemia), or a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia). Taken together, these signs are a clear indication of leukemia.
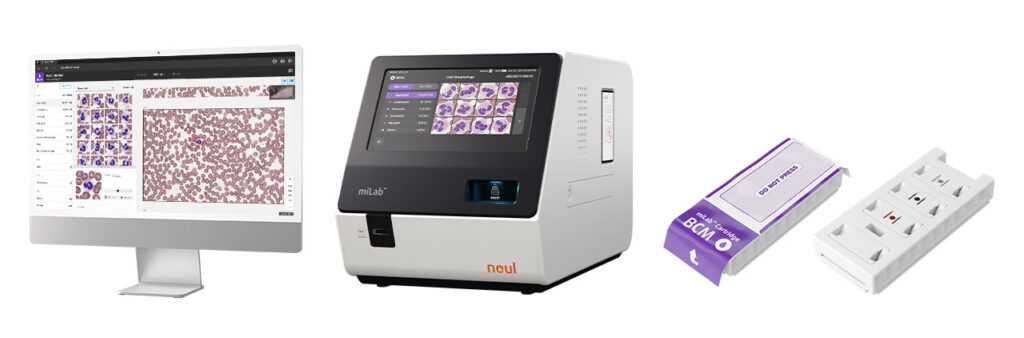
The Role of Automated Diagnostics in Leukemia Testing
Source: NOUL
Part of the problem with diagnosing leukemia is the manual diagnostic process. CBCs are relatively easy to perform; however, a blood smear is a laborious process requiring highly-trained teams and a full laboratory. Even with the right setup, there’s a risk of human errors when interpreting the results.
NOUL’s miLab™ BCM is a revolutionary alternative. It harnesses the power of AI to rapidly a leukemia blood smear. In a matter of minutes, the algorithm analyses the blood cells, detecting abnormal blood cells faster and more accurately than its human counterparts. The benefit? Leukemia patients get diagnosed early, giving a greater chance for treatment planning.
The miLab™ BCM is the only global product that combines both CBC-based screening and morphology testing, offering the full gamut of leukemia-related diagnostics. It’s a comprehensive platform for hematological testing, patching the gaps in less developed healthcare systems.
Conclusion

Source: Wikimedia Commons
Leukemia is a life-threatening blood cancer that requires timely testing to diagnose the condition early. The two primary tests are a complete blood count and a blood smear. The leukemia CBC results and blood smear detect changes in blood cell numbers and morphology, respectively.
Advanced diagnostic tools like NOUL’s miLab™ BCM play a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of healthcare providers by offering precise and efficient testing solutions. They’re the next step in accurate, efficient, and affordable diagnostics for leukemia and other hematological disorders.
Learn more about NOUL‘s products, how they work, and how they can improve your clinical practice. For further information and to explore how these innovative solutions can benefit your practice, visit our website or contact us directly.

