Most body cells have a nucleus, except mature red blood cells, which lack one.
Unfortunately, in some cases, nucleated red blood cells (nRBCs) can appear. It’s usually a sign of a life-threatening condition and indicates that immature blood cells that have not completed their development have found their way into circulation.
Detecting nRBCs early on is crucial to diagnosing the underlying condition, including leukemia, certain blood disorders, bone marrow dysfunction, and hypoxia. With the novel miLab™ BCM from NOUL, labs can now perform rapid and precise nRBC blood tests, ensuring levels are within the normal range.
What Are Nucleated Red Blood Cells?
 Source : Shutterstock
Source : Shutterstock
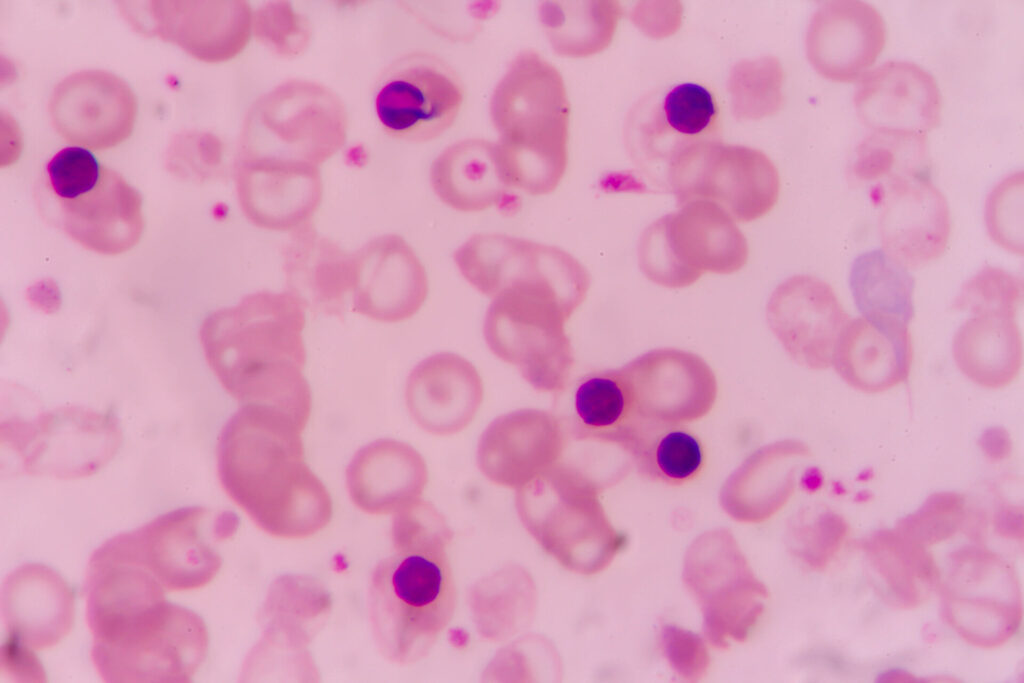
Nucleated red blood cells, or nRBCs, are immature blood cells that are not usually present in adults. Commonly found during fetal development, nucleated red cells are increasingly less common in people as the bone marrow fully matures.
A positive nRBC blood test often indicates a significant underlying condition. Normally, red cells expel their nucleus early in development. However, this can change if there’s severe stress on the bone marrow or circulation, causing the bone marrow to release nRBCs directly into the bloodstream.
Several different kinds of nRBCs exist depending on their stage of development. These include:
- Pronormoblast (Rubriblast) – The earliest stage, large with a deep blue cytoplasm.
- Basophilic Normoblast (Prorubricyte) – Slightly smaller, with a basophilic cytoplasm.
- Polychromatophilic Normoblast (Rubricyte) – Shows a mixed blue and pink cytoplasm due to hemoglobin accumulation.
- Orthochromatic Normoblast (Metarubricyte) – Mostly pink with a small, dense, dark nucleus that is often eccentrically located just before losing the nucleus to become a reticulocyte.
The presence of these developing blood cells, sometimes referred to in medical contexts as erythroblasts, requires further investigation to determine the underlying cause. Generally, the earlier the nRBC is in development, the more profound the problem is.
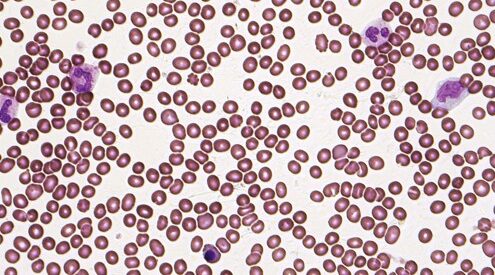
The nRBC Blood Test: Purpose and Application
 Source : NOUL
Source : NOUL
The nRBC blood test helps identify conditions like anemia, leukemia, and bone marrow issues.
Common conditions linked to elevated nRBC levels include:
- Hematologic Disorders: Includes bone marrow failure, leukemia, and myeloproliferative diseases, which disrupt normal marrow function.
- Trauma or Acute Stress: Severe blood loss or intense stress triggers nRBC production as a compensatory response.
- Neonatal Conditions: Elevated nRBCs in premature infants due to immature bone marrow function.
- Disease Monitoring: nRBC counts help monitor disease progression and the effectiveness of treatments like chemotherapy.
Interpreting nRBC Blood Test Results
Healthy adults typically have zero nRBCs, and the nucleated blood cells normal range is considered 0. Any presence of nRBCs warrants further investigation.
That being said, it’s important to differentiate between absolute and relative values. The nRBC blood test can be represented by either the total number of nRBCs (the absolute nRBC count) or as a percentage of the overall white blood cells (the relative nRBC count).
An absolute nRBC considers levels higher than 0.02 x 109 /L to be beyond the nucleated blood cells normal range. Other studies put this even lower at 0.003 x 109 /L. On the other hand, the percentage is written as a value per 100 white blood cells. The ideal result is 0.3/100 WBC. (0.3%)
Remember, elevated nRBC levels are the only significant clinical finding. A low or negative nRBC level simply indicates the patient’s red blood cell production is functioning normally.
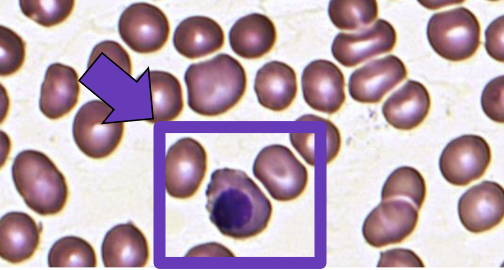
Clinical Implications of nRBC Findings
 Source : NOUL
Source : NOUL
An abnormal absolute nRBC results require further tests, including a CBC, to help diagnose conditions like anemia, leukemia, or bone marrow dysfunction.
Usually, a complete blood count (CBC) provides a good insight into the condition, giving an indication of either anemia, leukemia, or bone marrow dysfunction. This could be represented by either low RBC levels or low or high WBC levels.
As nRBCs indicate bone marrow stress, it’s important that a positive result is given immediate attention. Only by acting early can doctors effectively treat conditions like leukemia or bone marrow failure. However, nRBCs can also act as a prognostic factor, charting the progression of leukemia or other conditions.
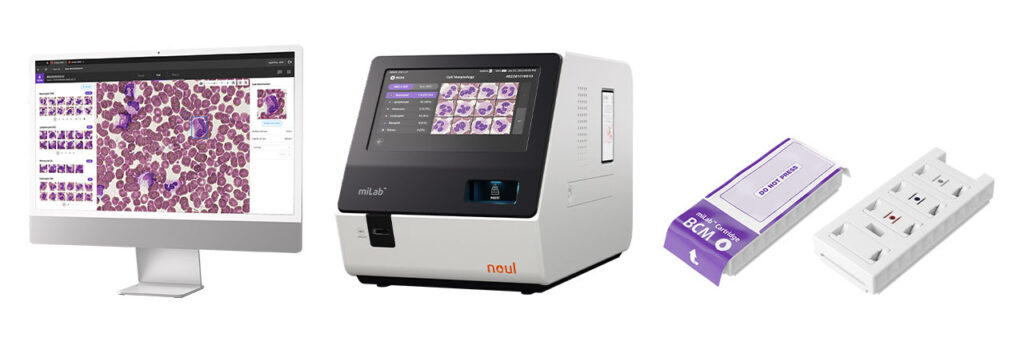
The Role of Technology in nRBC Detection: How miLab™ BCM Enhances Diagnostics
Source : NOUL
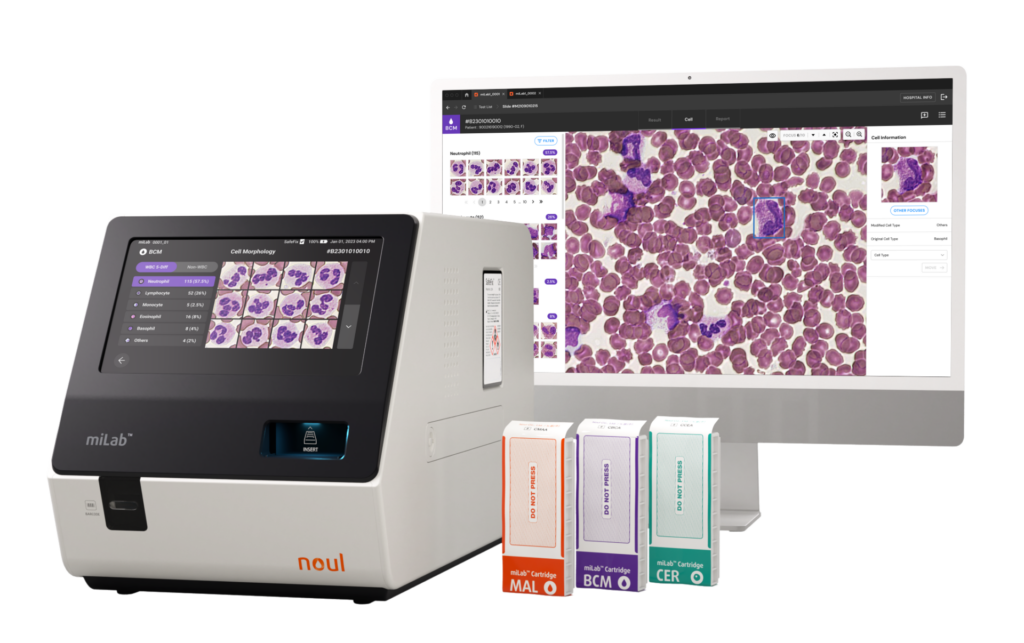
miLab™ BCM, an AI-powered diagnostic tool by NOUL, revolutionizes nRBC testing. This platform provides comprehensive blood analysis, automating the entire testing process, from blood smear to AI analysis.
Usually, this process involves multiple complex steps and significant manual labor. However, by integrating these processes into a single, streamlined workflow, miLab™ BCM not only saves time but also reduces the likelihood of human error.
Some notable features include:
- AI-powered Analysis: The embedded AI technology pre-classifies blood cells, enhancing the accuracy and speed of nRBC detection. This automated analysis allows for rapid diagnostic decisions, which is crucial for effective treatment planning.
- Compact and Efficient: Its design is highly portable and user-friendly, making it suitable for a variety of healthcare environments, from small clinics to large hospitals.
- High Diagnostic Accuracy: With its advanced imaging and analysis capabilities, miLab™ BCM quickly identifies abnormalities in blood cells, providing critical information for diagnosing various conditions.
With more tests performed and greater accuracy, the miLab™ BCM has the potential to revolutionize healthcare testing, as evidenced by various studies demonstrating its effectiveness in improving diagnostic speed and accuracy. It can help lower the overall cost of diagnostics while delivering better patient outcomes. It’s truly a game-changing technology.
Why Accurate nRBC Testing Matters for Healthcare Provides
 Source : NOUL
Source : NOUL
Nucleated red cells are immature red blood cells in circulation. The presence of these cells indicates either anemia or some problem with the bone marrow. The nucleated blood cells normal range is usually 0 (or some extremely low level). Any presence of nRBCs requires further testing.
Unfortunately, current testing methods are often beleaguered by long turnaround times, high error rates, and a reliance on specialized equipment. NOUL‘s miLab™ BCM represents the cutting-edge of AI medical diagnostics. With its fast, accurate, and AI-powered nRBC blood tests, it solves many of these ongoing challenges.
Learn more about the miLab™, or get in touch with our team to find out how we can upgrade your laboratory.

