본 웹사이트는 사용자에게 최상의 사용자 경험을 제공하기 위해 쿠키를 사용합니다. 쿠키 정보는 브라우저에 저장되어 사용자가 당사 웹사이트로 돌아올 때 사용자를 인식하고, 사용자가 가장 흥미롭고 유용하다고 생각하는 웹사이트 섹션을 당사 팀이 파악하는 데 도움을 주는 등의 기능을 수행합니다.
디지털 자궁경부세포분석 솔루션, miLab™ CER

Pap smear 검사 과정을 자동화한
AI 기반 디지털 세포진 솔루션
자궁경부암 진단 솔루션 miLab™ CER은 자궁경부세포검사의 복잡한 공정과 전문 인력 의존도를 대폭 줄이며, 고품질 진단을 자동화한 혁신적인 디지털 세포진 솔루션으로 주목받고 있습니다. miLab™ CER은 WHO-UNITAID 공동 기술현황 보고서(2024)*에서 AI 기반 알고리즘을 통해 Bethesda 체계에 따라 세포진 결과를 슬라이드 단위로 제공하는 컴퓨터 보조 세포진 진단 시스템으로 언급되었습니다.
- * Screening and treatment of precancerous lesions for secondary prevention of cervical cancer: technology landscape (2024)
- 다운받기
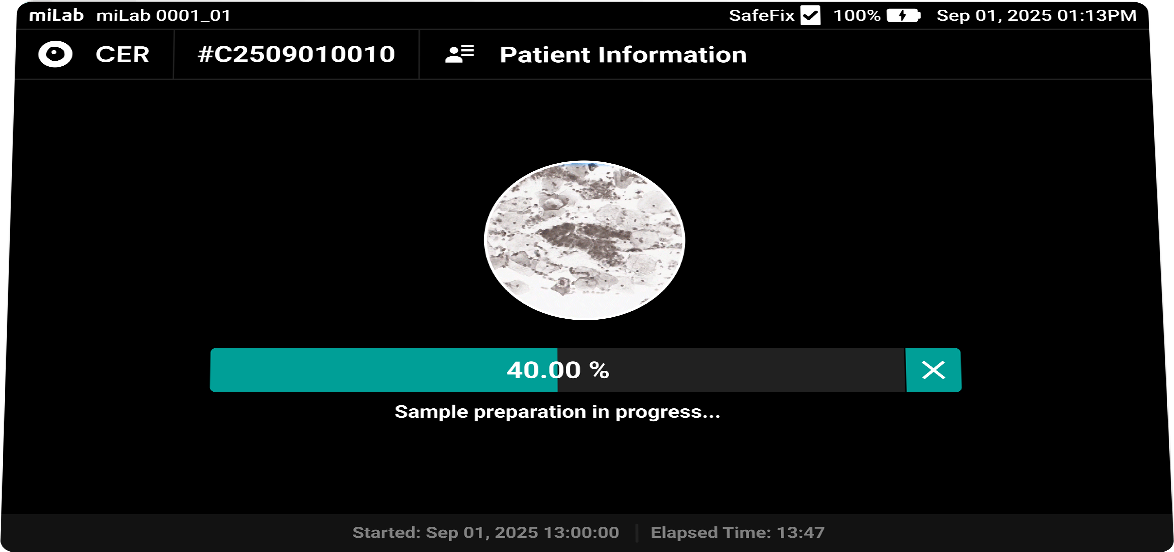
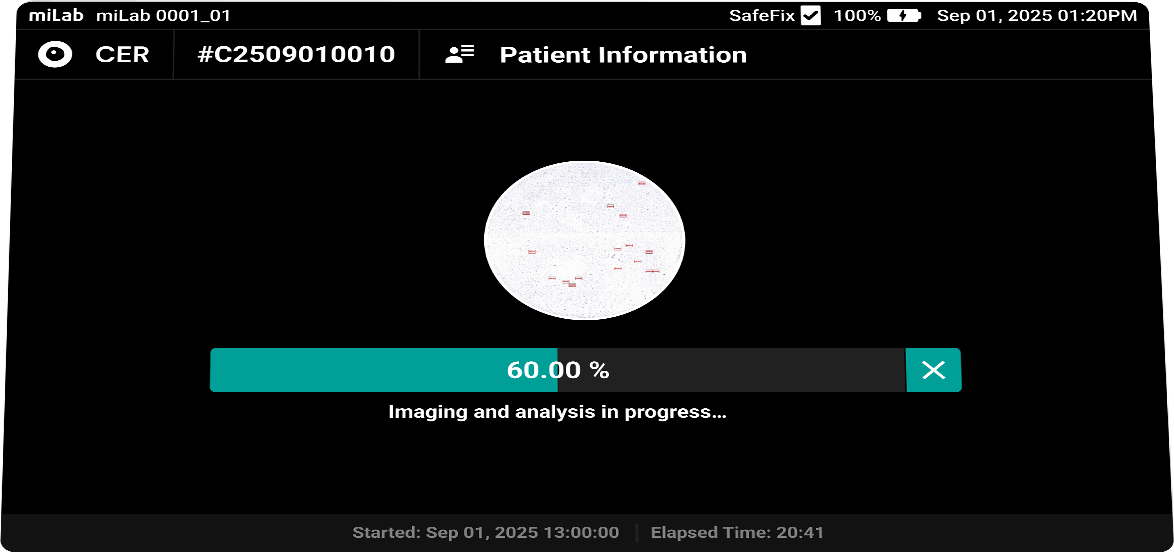
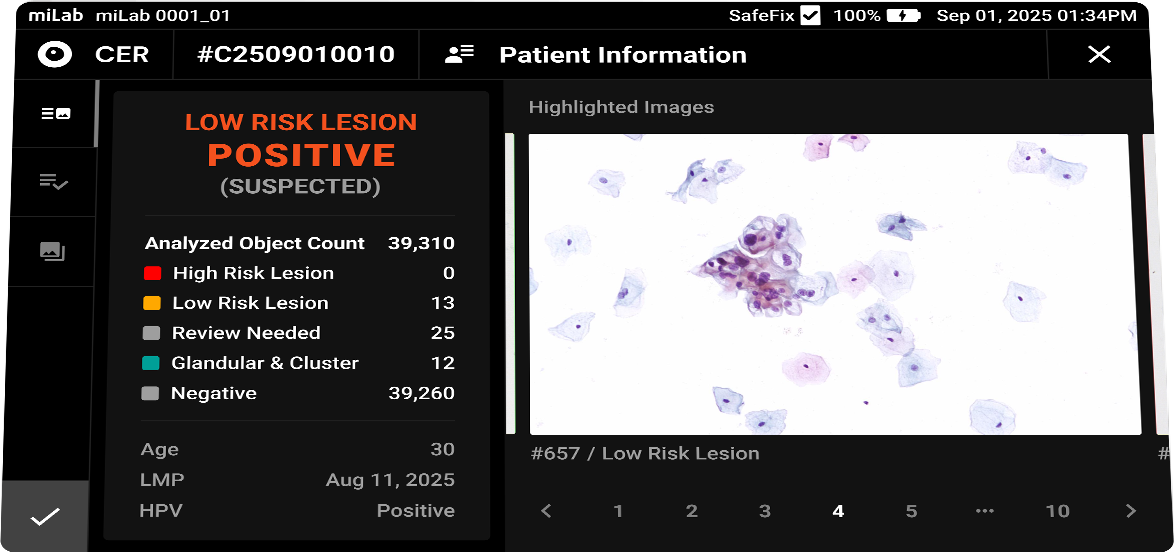
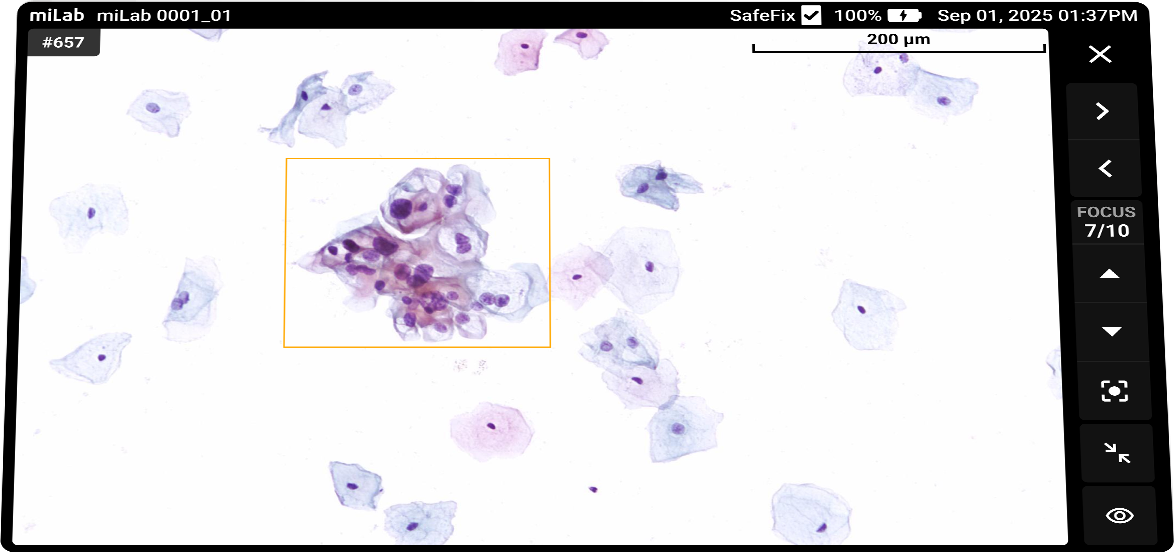
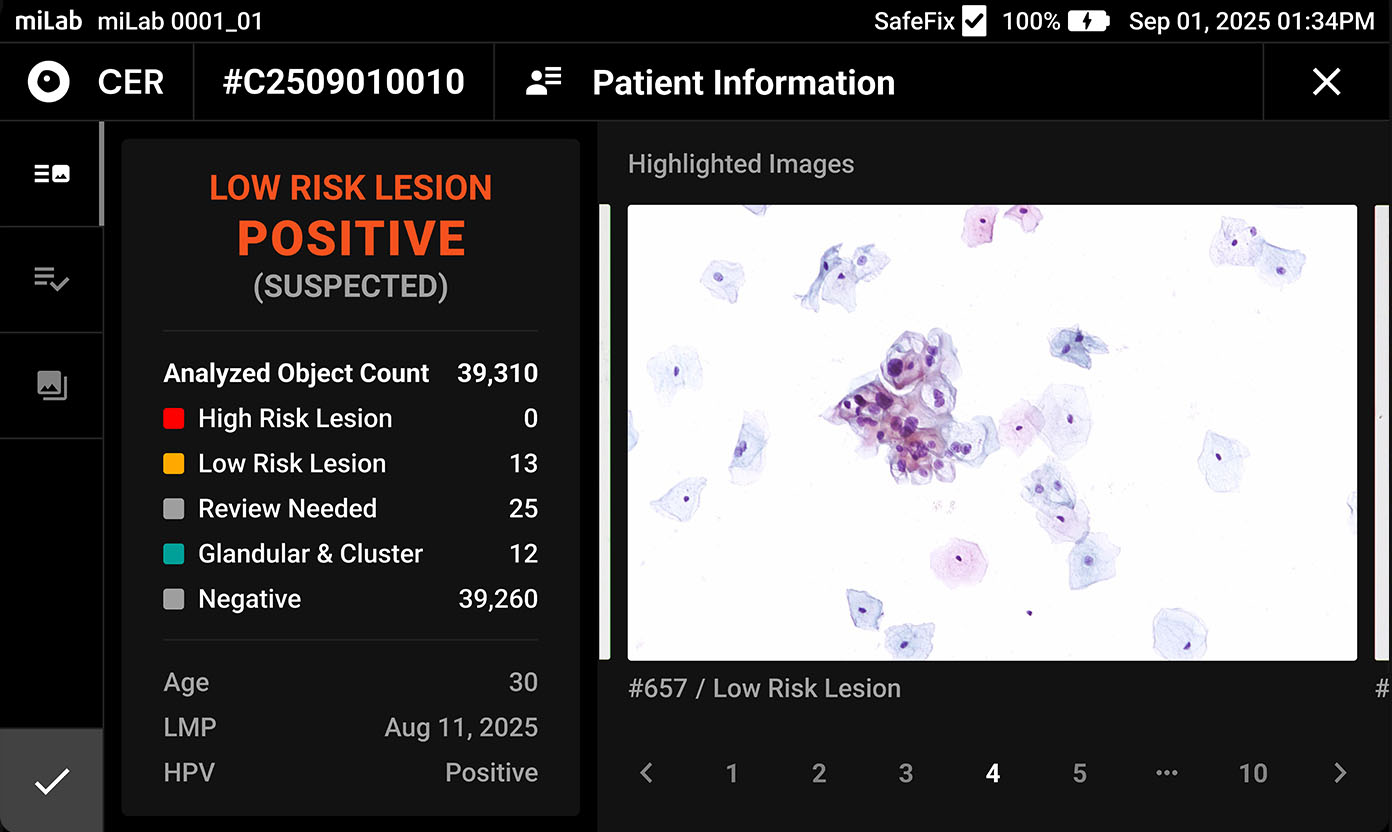
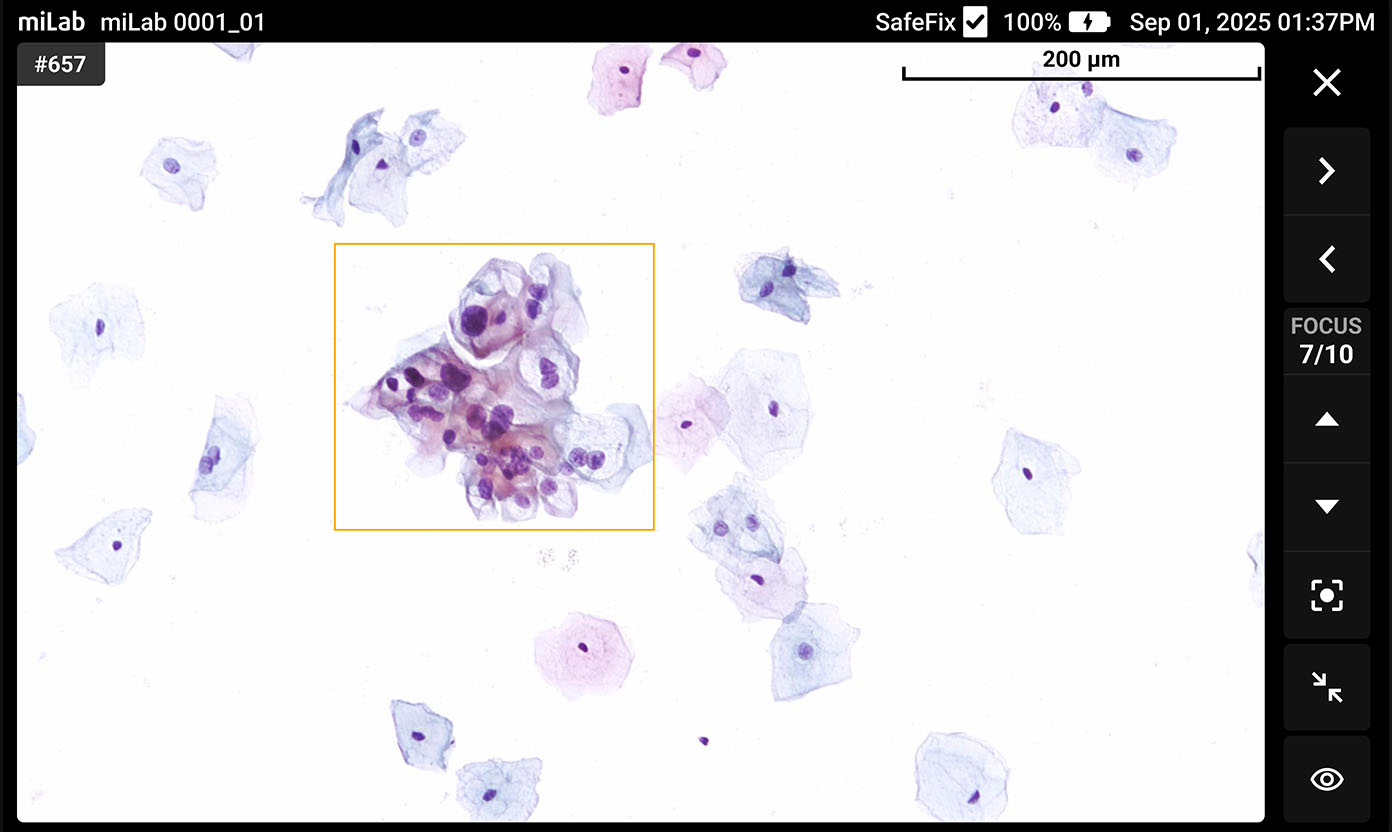
디지털 자궁경부세포분석 솔루션 miLab™ CER은, 도말된 자궁경부세포 슬라이드를 염색, 이미지 촬영, AI 분석까지 자동으로 수행하여 기존의 복잡한 검사 과정과 이에 필요한 인프라를 하나의 디바이스로 대체하였습니다. 디바이스 내에서 촬영된 자궁경부세포 이미지는 AI 알고리즘이 평균 약 25,000개의 세포를 분석하고, Bethesda 체계에 따라 분류하여 전암(pre-cancer) 및 암(cancer) 소견을 탐지합니다. 의료 전문가는 Viewer를 통해 현장 또는 원격으로 결과를 확인하고 재분류할 수 있으며, 그 결과를 바탕으로 현장 치료 또는 상급 병원 진료 연계 여부를 신속하고 정확하게 판단할 수 있습니다.
miLab™ CER은 자궁경부암 조기 검진을 받기 어려운 여성들의
의료접근성 향상에 집중합니다.
자궁경부암은 전 세계 여성에게서 네 번째로 많이 발생하는 암이며,조기 검진을 통해 예방이 가능한 질환입니다.
그러나 많은 여성들이 진단 인프라 부족과 전문 인력의 부재로 인해, 조기 검진을 받기 어려운 환경에 놓여 있습니다.
WHO는 2045년까지 자궁경부암 발생률을 2020년 대비 42%까지 줄이는 것을 목표로 설정하고, 국제사회의 적극적인 참여와 기술적 지원을 요청하고 있습니다.
전세계 자궁경부암 주요 현황
* 2021년 기준
대표적인 자궁경부암 진단검사 방식으로는 Pap smear 검사와 HPV 검사가 있습니다. 그러나 이러한 기존 검사 방식은 각각의 장점에도 불구하고 인프라, 운영 비용, 결과의 신뢰도 측면에서 많은 한계가 존재합니다.
현재 자궁경부암 진단 기술의 한계
- 중저소득국가에서는 정확한 결과 판독이 가능한 전문 인력 부족 문제 심각
- 아프리카 국가들은 인구수 대비 병리학자 비율이 평균 100만명당 1명 미만으로 미국 대비 1/50 수준
- 캐나다 등 고소득국가에서도 검사 수요 대비 전문 검사 인력 부족율 증가 추세
- 자궁경부세포검사를 위한 파파니콜라우 염색은 7종류의 시약과 20단계의 세부 작업 단계로 구성되어 전문 인력의 숙련도가 매우 중요
- 검사 환경 및 검사자에 따라 휴먼에러 발생 가능성 상존
- 진단검사 소요 시간 최소 2일에서 60일 이상
- 정확한 진단을 위한 인력, 인프라, 장비 등 워크플로우 비용 높음
- 자궁경부암 발생의 90%를 차지하는 중저소득국가에서는 자원 제약으로 Pap smear 검사를 위한 진단 검사실 구축 어려움
- HPV 검사만으로는 자궁경부 전암/암 단계 판별이 불가하여 과잉치료 문제 발생
표준 염색 프로세스 수행, 세포별 디지털 이미지 확보, AI 결과 분석,
이 모든 과정을 전자동으로
- 혁신적인 고체염색 기술로 표준적인 Pap smear 방식을 전자동으로 구현
- 별도의 인프라 투자 없이 디바이스 하나로 진단검사실 기능 대체
- AI 분석을 바탕으로 전암/암 단계별 세포의 사전 분류 결과 제공
- 기존 워크플로우의 획기적인 개선
- 파파니콜라우 염색 단계를 20단계에서 5단계로 획기적인 축소 및 자동화
- 염색, 세척, 건조를 비롯한 샘플 프렙 과정과 이미지 판독 과정의 완전 자동화
- 당일 검사 및 원격 진단 서비스 지원
- 검체 채취 현장에서 1시간 이내에 검사 결과의 직접 확인이 가능하며, 검사 결과에 따라 신속한 임상 대응이 가능
- 세포별 디지털이미지가 기록으로 저장되며, 원격 접속을 통한 원격 진단 서비스 지원 가능
- 중저소득국가에서 신뢰도 높은 조기 진단 검사 수행 가능
- 자원 제약 환경에서 신뢰도 높은 Pap smear 검사 방식 구현
- 자궁경부세포의 형태학적 특성을 기반으로 현장에서 병변 여부 판단의 명확한 근거 제공으로 과잉 치료 예방
검체 채취가 가능한 의료시설이라면, 이제 miLab™ CER을 통해 자궁경부암 선별검사를 자체적으로 효율적이고 정확하게 수행할 수 있습니다.
- 1. 자체적으로 Pap smear 검사를 수행하기 원하는 의료기관
- 타깃 고객
- 1차 자궁경부암 선별검사 방식이 Pap smear인 국가에서, 자궁경부세포 채취는 가능하나, 진단검사실이 없어 자체 Pap smear 검사 수행은 불가능한 의료기관
- 기대 가치
- Pap smear 검사 추가로 수익 창출 기회 확대
- Background
- 한국을 포함해 많은 국가에서 자궁경부암 선별검사를 국가지원프로그램으로 운영하고 있으며, 국가별로 다수의 의료기관들이 자궁경부암 선별검사 프로그램에 참여하고 있습니다. 그렇지만 이중에서도 자체적인 진단검사실을 보유한 의료기관은 소수에 불과합니다. 대부분 의료기관은 자궁경부세포를 채취한 후, 인근의 전문진단검사실로 진단 검사 위탁을 맡기는 방식으로 검사를 수행하고 있습니다.
- Problem
- 자체적으로 Pap smear 검사를 수행하지 못하는 의료기관은 외부 진단검사실로 검체를 의뢰하게 되며, 그에 따라 비용을 지불하게 됩니다. 진단검사 결과를 받기까지는 외부 진단검사실의 검사 일정에 따라 통상 7일 정도에서 많게는 60일 이상 소요되기도 합니다.
- Use-Case
- 이같은 의료기관에서는 miLab™ CER 도입으로 간단한 작업 단계 추가로 자궁경부세포 채취는 물론, 자궁경부암 선별검사까지 이어서 수행할 수 있습니다. miLab™ CER은 검체 염색부터, 디지털이미지 촬영, AI 분석 과정을 자동화한 솔루션이기 때문에, 의료기관에서는 채취한 자궁경부세포를 슬라이드 위에 도말하고 고정하는 과정이 추가됩니다.
- Benefits
- 해당 유형의 고객들은 miLab™ CER 도입으로 자궁경부암 선별검사를 받으러 온 환자들에게 보다 신속하게 선별검사 결과를 공유할 수 있습니다. 또한, 기존에는 수행하지 않았던 추가 검사를 고객에게 제공함으로써 수익 창출의 기회를 확대할 수 있게 됩니다.
- 2. Pap smear 검사의 생산성을 높이려는 의료기관
- 타깃 고객
- 전문 인력의 노동집약적인 방식으로 Pap smear 검사를 수행하는 의료기관
- 기대 가치
- Pap smear 검사 자동화로 워크플로우 개선 및 생산성 향상
- Background
- 일반적인 Pap smear 검사는 노동집약적인 방식으로 검사가 수행됩니다. 샘플 프렙 단계에서는 혈액 도말, 고정, 염색, 세척, 건조 등 과정을 수작업으로 진행하며, 현미경 분석 단계에서는 전문 인력이 현미경을 통해 자궁경부세포의 형태와 분포를 하나씩 눈으로 확인하는 방식으로 진행됩니다. 특히, Papanicolaou 염색은 20단계로 이루어지는 등 복잡도가 높은 작업입니다.
- Problem
- 노동집약적인 방식으로 인해 Pap smear 검사 건수가 증가할수록 전문 인력이 느끼는 육체적 피로감은 증가하게 됩니다. 전문 인력의 육체적 피로감이 증가할수록, 실수 등 휴먼에러 발생 가능성 역시 높아지게 됩니다. 또한, 의료기관마다 Pap smear 검사를 위한 작업 표준이 고정되어 있기 때문에, 정해진 인원과 시간으로 보다 많은 검사를 수행하기도 어려운 상황입니다.
- Use-Case
- Pap smear 검사의 생산성 향상을 기대하는 의료기관에서는 miLab™ CER을 도입해 전문 인력이 수행하던 작업의 일부를 자동화할 수 있습니다. miLab™ CER은 가장 복잡하고 실수하기 쉬운 Papanicolaou 염색부터, 디지털이미지 촬영, AI 분석 과정을 자동화합니다. 전문 인력은 복잡한 염색을 직접 수행하거나, 일일이 자궁경부세포를 현미경으로 찾을 필요 없이, 모니터 화면을 통해 분석된 결과를 검토하고 최종 확인하는 역할에 집중할 수 있게 됩니다. 또한 전문 인력이 근무하지 않는 야간/주말 시간에도 miLab™ CER을 통한 자동 분석이 가능하고, 해당 분석 결과는 데이터베이스에 축적할 수 있습니다. 전문 인력은 다음날 출근하여 효율적으로 분석 결과를 검토하고 최종 확인할 수 있습니다.
- Benefits
- 해당 유형의 고객들은 miLab™ CER 도입으로 정해진 인원과 시간으로 기존 대비 획기적으로 검사 수행 건수를 증가시킬 수 있습니다. 자궁경부암 선별검사 수요가 증가하는 의료기관에서는 전문 인력의 추가 고용 없이도 miLab™ CER 도입으로 증가하는 검사 수요에 대응할 수 있습니다. 이같은 생산성 향상의 가치는 전문 인력의 인건비가 높은 고소득 국가에서 더 높습니다.
- 3. Pap smear 검사의 정확도를 높이고자 하는 의료기관
- 타깃 고객
- 자체적인 진단검사실을 보유하고 있지만, 숙련도가 낮은 전문 인력 중심으로 Pap smear 검사를 수행하는 의료기관
- 기대 가치
- 품질 보증 및 품질 관리 체계 강화로 Pap smear 검사 신뢰도 향상
- Background
- 일반적으로 Pap smear 검사를 수행하는 전문 인력은 국가 차원에서 전문 의료인으로서 전문화된 지식과 풍부한 경험을 갖추도록 요구합니다. 대학 이상의 전문 교육 이수와 국가 자격시험 통과는 물론이고, 정기적인 실무 교육/훈련을 받도록 하고 있습니다. 한국 등 의료교육 시설 및 체계가 잘 갖춰진 국가에서는 전문 인력의 수준이 높게 유지되고 있으나, 중저소득국가에서는 의료교육 시설 및 체계가 충분하지 못한 상황입니다.
- Problem
- Pap smear 검사는 노동집약적인 방식으로 수행되기 때문에 전문 인력의 숙련도에 따라 분석 및 판단 결과에서 편차가 크게 나타납니다. Pap smear 검사의 분석 결과가 잘못될 경우에는 환자에 대한 잘못된 진단과 치료로 이어지게 됩니다. 의료기관은 고용된 인력이 정확한 분석 결과를 제공하고 있는지를 확인하기 위해서, 여러 전문 인력이 동시에 검사를 수행하도록 하여 그 결과를 비교해 보거나, 검증된 전문 인력이 해당 분석 결과를 검증하도록 할 수 있습니다. 그렇지만 이같은 방법은 모두 전문 인력 고용을 더 확대하거나, 전문성이 검증된 인력을 고용하는 등 추가적인 비용 부담이 발생하게 됩니다.
- Use-Case
- Pap smear 검사에 대한 정확도를 높이고자 하는 의료기관에서는 miLab™ CER을 품질 관리 체계에 포함할 수 있습니다. miLab™ CER은 Papanicolaou 염색부터 AI 분석까지 Pap smear의 핵심 과정을 표준화하였습니다. 따라서 전문 인력이 수행한 Pap smear 검사 결과와 miLab™ CER 결과를 비교함으로써 전문 인력의 검사 결과 신뢰도를 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한, 숙련도가 낮은 전문 인력에게는 miLab™ CER에서 생성된 디지털데이터를 교육/훈련 자료로 활용할 수도 있습니다.
- Benefits
- 해당 고객은 miLab™ CER 도입으로 Pap smear 검사 품질 관리 체계를 강화하고, 이를 통해 기존 전문 인력의 검사 신뢰도를 검증할 수 있습니다. 또한, miLab™ CER의 디지털데이터를 교육/훈련 자료로 활용하면서, 의료 교육 시설과 체계가 부족한 중저소득국 환경에서 판독 전문성을 강화할 수 있습니다.
- 4. 원격으로 Pap smear 검사를 수행하고자 하는 의료기관
- 타깃 고객
- 자궁경부세포 채취는 가능하지만, 자체적인 진단검사실을 보유하고 있지 않으며, 인근 지역에서 상급 의료기관 및 전문 인력 부재로 위탁 검사 의뢰가 불가능한 의료기관
- 기대 가치
- 기존 의료체계에서 소외된 환자들에 대한 의료접근성 강화
- Background
- 물리적 접근이 어려운 도서산간 지역 혹은 전문 교육 시설이 부족한 중저소득국에서는 Pap smear 검사 수행을 위한 전문 인력이 충분하지 않습니다. 일부 지역에서는 Pap smear 검사 수행이 가능한 의료기관이 존재하지 않는 경우도 있습니다.
- Problem
- Pap smear 검사 수행이 어려운 지역에 거주하는 주민들은 자궁경부암 선별검사를 받기 위해서, 시간과 비용을 들여 먼 거리를 이동해야 하는 불편이 존재합니다. 이같은 불편 때문에 해당 지역의 주민들은 자궁경부암 선별검사를 주기적으로 받지 못하고, 질병 발생 위험에 노출될 가능성이 증가할 수 있습니다.
- Use-Case
- 해당 지역에서 자궁경부세포 채취가 가능한 의료기관에서는 miLab™ CER을 도입해, 원격에 위치한 전문 인력에게 디지털데이터를 전송하고 정밀 판독을 요청하는 방식으로 활용할 수 있습니다.
- Benefits
- 해당 고객은 miLab™ CER 도입으로 자궁경부암 선별검사에 대한 주민들의 접근성을 향상시킬 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 주민들의 자궁경부암 발생 여부를 조기에 진단하고, 적절한 치료를 받을 수 있도록 도와줄 수 있습니다.
- 5. 신뢰도 높은 자궁경부암 선별검사 시스템으로 전환하고자 하는 정부
- 타깃 고객
- 자궁경부암 발생건수 및 사망건수가 심각한 상황이나, 국가 차원의 진단검사실 인프라와 전문 인력 부족으로 자궁경부암 선별검사 방식으로 VIA 검사에 의존하고 있는 중저소득국 정부
- 기대 가치
- 인프라와 전문 인력 투자를 최소화하면서, 국가 내 자궁경부암 발생건수 및 사망자수 감소를 위한 신뢰할 수 있는 자궁경부암 조기 검진 기반 마련
- Background
- Pap smear 검사는 자궁경부암 선별검사로 가장 보편적이고 정확한 검사 방법이지만, 진단검사실 인프라와 전문 인력에 의존해야 한다는 한계가 있습니다. 전세계 50여 개의 중저소득국에서는 자궁경부암 선별검사 방법으로 자원 의존도가 낮은 VIA 방식을 활용하고 있거나, 정부 차원의 선별검사 방식을 특정하지 않고 있습니다.
- Problem
- VIA 방식은 검사자가 육안으로 확인하므로 과학적이지 않은 검사 방식입니다. 낮은 정확도와 검사자에 따른 주관적 판단 우려로 WHO에서 권고하지 않는 선별검사 방식이기도 합니다. VIA 방식을 자궁경부암 선별검사로 활용하는 국가에서는 환자의 정확한 상태 확인에 어려움이 있어, 자궁경부암의 조기 진단과 조기 치료를 통한 피해 예방이라는 목적을 달성하기에 적합하지 않을 수 있습니다.
- Use-Case
- VIA 방식 혹은 자궁경부암 선별검사를 특정하지 않은 정부에서는 miLab™ CER을 활용해 Pap smear 검사를 국가 표준 자궁경부암 선별검사로 전환할 수 있습니다. miLab™ CER은 Pap smear를 수행하기 위한 의료기관의 진단검사실 인프라 투자를 최소화 하며, 워크플로우 개선 및 원격 진단 서비스 제공을 통해 소수의 전문 인력을 가장 효율적으로 활용할 수 있는 자궁경부암 선별검사 시스템 구축할 수 있습니다. 또한, 디지털데이터를 기반으로 전문 인력의 교육과 훈련을 위한 풍부한 자료를 제공함으로써, 국가 내 전문 인력 양성에도 기여할 수 있습니다.
- Benefits
- 해당 국가들은 miLab™ CER 도입으로 최소한의 진단검사실 인프라와 전문 인력 투자로 가장 보편적이고 신뢰도 높은 Pap smear 검사로 자궁경부암 선별검사 방식을 전환할 수 있게 됩니다. 이를 통해 국민들의 자궁경부암 발생 여부를 조기에 정확하게 진단하고, 적절한 치료를 받을 수 있는 공공보건 체계를 구축할 수 있습니다.
- 6. 기타 사례
miLab™ CER은 다양한 환경과 상황에 광범위하게 적용될 수 있는 솔루션입니다. miLab™ CER 제품의 사용에 관심이 있다면 언제든 연락주세요. 여성의 자궁경부암 조기/정기 검진을 위한 성공 사례를 miLab™ CER와 함께 만들어나갈 수 있습니다.
Stain, Scan, and
Classify cells in 20 mins
- miLab™ CER Specification
- Sample Preparation
Sample type Cervicovaginal sample smeared with LBC (Liquid-Based Cytology) Staining type Gold-standard Papanicolaou staining
- Imaging
Lens 20x magnification Focus Provides 10 z-stack images with the best focus for each cell Imaging Automatically an average of 25,000 cells across the entire LBC smear field
- Analysis
Classification NILM, ASCUS, LSIL, ASC-H, HSIL, SCC Images Field-binding images classified based on the presence or absence of atypical cells
- Total Test Time
up to 30 minutes
- Remote Review
Viewing Functions AI classification, Field images, Reclassification and Report
- Product Code
Product Code miLab™ Platform DMLA miLab™ Cartridge CER CCEA miLab Viewer™ SMVA SafeFix™ CER CSCA miLab™ Slide Case ASCA